Custom services
MGB Probes Synthesis
Increase the specificity of your qPCR Assay with our license-free molecular probes.
We offer custom MGB Eclipse™ probes with dyes covering all qPCR channels.
From Deep Blue to IR Dyes
Our chemical experts are fully trained to synthesize MGB Probes conjugated to a large range of fluorophores.
According to your qPCR platform, we can provide you with molecular probes ranking from deep blue fluorescence to infra-red.
Commercial use of qPCR Probes labeled with ATTO, Yakima Yellow® or Texas Red® fluorescent dyes may be subject to IP,
please check out our License statements.
please check out our License statements.
What are the advantages
of the MGB probe technology?
Specific
MGB increases the Tm of a probe thanks to its minor groove binding ability and offer a very high specificity toward its complementary sequence.
Sensitive
MGB-Eclipse™ Probes display a very high signal to noise ratio ensuring the detection of low copy targets.
Efficient
License-free MGB-Eclipse™ Probes are perfectly suited for patient management and diagnostic of pathogens.
The best quality/price ratio on the market
Benefit from our know-how at the best price. We are committed to providing our customer with the best quality product at the most affordable price. As an official supplier of ELITech Group, we use quality raw materials and produce very efficient fluorescent molecular probes.
At your side all along your project
We deliver MGB Probes for in vitro diagnostic applications such as patient management. We assist our customers in their strategy to commercialize their own diagnostic kits and offer them the best approach in compliance with the regulations.
What are MGB Probes?
An MGB probe is a DNA probe with a minor groove binder conjugated at the 3’end, and a fluorescent reporter dye at the 5’end. Additionally, an Eclipse™ quencher (EDQ) is linked to the 3’end.
The presence of the MGB moiety stabilizes the duplex probe-target, resulting in an increased Tm. A shorter probe can be designed, reinforcing the specificity of the qPCR Assay.
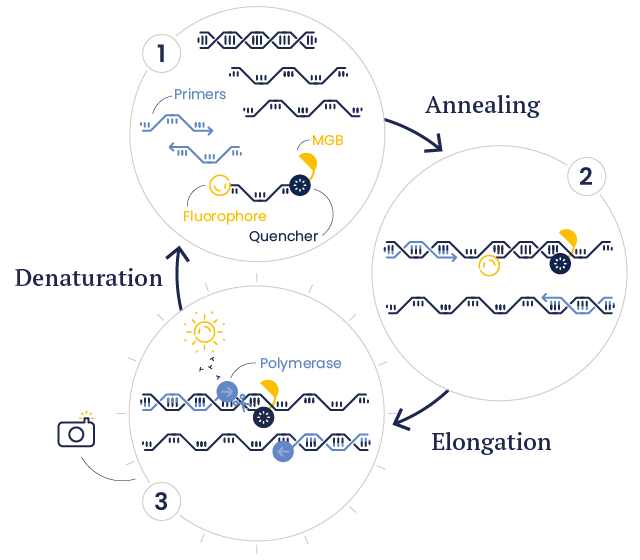
MGB Probe Principle
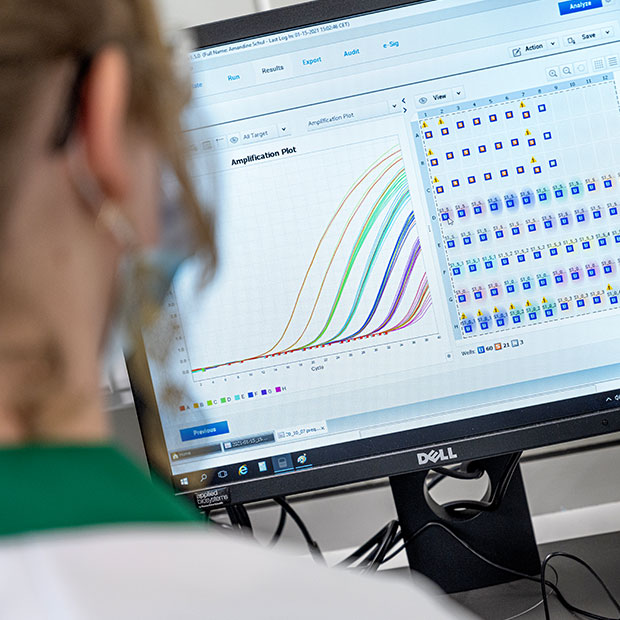
Based on the TaqMan® technology, the 5'-3' exonuclease activity of the Taq DNA polymerase cleaves the fluorophore from the probe during the amplification process. Since the fluorophore is no longer subjected to FRET quenching, it starts to fluoresce. This fluorescence can be measured, and the level is directly proportional to the amount of target DNA accumulating during the PCR reaction